An Action Potentional Can Best Be Described as
An action potential is a predictable change in membrane potential that occurs due to the open and closing of voltage gated ion channels on the cell membrane. Na channels open at the beginning of the action potential and Na moves into the.

The Threshold Potential For Generation Of An Action Potential In A Postsynaptic Cell Molecular Cell Biology Cell Biology Biology Molecular
It is the electrical signal that nervous tissue generates for communication.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11524/Action_potential_ions.png)
. Inside becomes positive relative to the outside. An action potential is a brief only a few milliseconds reversal of the membrane potential Vm. Action potential is passively propogated down the axon.
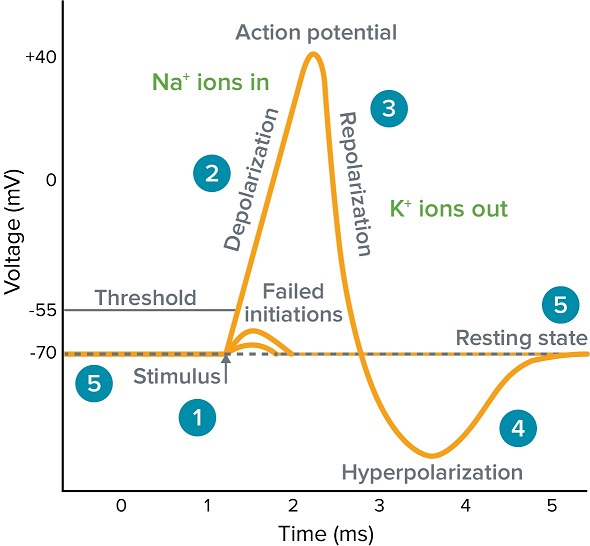
An action potential occurs when a portion of the membrane rapidly depolarizes and then repolarizes again to the original resting state. An action potential is generated when membrain is depolarization to the threshold value. The action potential often reaching as high as 100 mV.
Action potential is propagated over the muscle cell membrane. Permeability of the membrane translates to the action of the ion channels in allowing certain ions to enter the cell which would otherwise not be possible in the normal resting stage. C once membrane potential reaches threshold an action potential will be generated and that action potential will always be the same magnitude.
In response to a signal from another neuron sodium- Na and potassium- K gated ion channels open and close as the membrane reaches its threshold potential. These two properties contribute to which characteristic of action potentials. A neuron a nerve cell is the basic building block of the nervous system.
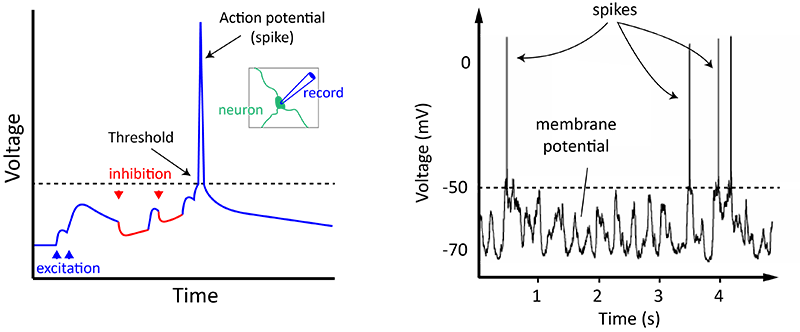
Neuron graded potential description. It can be a small or large reduction in the membrane potential If enough Na gates open the membrane potential of the dendrites will be reduced to the threshold potential of -55mv or less This will cause the rest of the neuron to fire ie. It is the electrical signal that nervous tissue generates for communication.
Action potential the brief about one-thousandth of a second reversal of electric polarization of the membrane of a nerve cell neuron or muscle cell. D following an action potential the membrane will be repolarized by the opening of a potassium channel. The creation of a brain signal.
Action potentials are conducted without any loss of signal strength. Because the number of Na ions moved outside the cell is greater than the number of K ions moved inside the cell is more positive outside than inside. The action potential is an explosion of electrical activity that is created by a depolarizing current.
Neuron membrane potentials questions 2. This process which occurs during the firing of the neurons allows a nerve cell to transmit an electrical signal down the axon a. Action potential an explosion of electrical activity thats created by a depolarizing current large brief reversal in polarity of an axon.
An action potential If only a few Na gates open the membrane potential may not be reduced enough. Key facts about the action potential. Neuron resting potential mechanism.
Neuron graded potential mechanism. At rest the Vm of a neuron is around 70 mV closer to the equilibrium potential for potassium VK but during an action potential Vm transiently approaches 50 mV closer to the equilibrium potential for sodium VNa. What has been described here is the action potential which is presented as a graph of voltage over time in.
During an action potential ions cross back and forth across the neurons membrane causing electrical changes. That property is called the excitability. It is defined as a brief change in the voltage across the membrane due to the flow of certain ions into and out of the neuron.
Neuron resting potential description. An action potential AP is the mode through which a neuron transports electrical signals. Only neurons and muscle cells are capable of generating an action potential.
An action potential occurs when a neuron sends information down an axon away from the cell body. An action potential is defined as a sudden fast transitory and propagating change of the resting membrane potential. As an action potential nerve impulse travels down an axon there is a change in electric polarity across the membrane of the axon.
Action potential follow the all or none rules View the full answer. In this article we will discuss how an action potential is generated and how conduction of an action potential occurs. Electrically Active Cell Membranes.
Sometimes called a propagated potential because a wave of excitation is actively transmitted. The basis of this process is the action potential. The area between the pre-synaptic nerve cell and the post-synaptic muscle cell is termed the synaptic cleft.
A chemical change occurring in the brain. It is the electrical signal that nervous tissue generates for communication. The process is initiated by a threshold level stimulus such as a nearby change in membrane potential threshold potential local.
When neurons transmit signals through the body part of the transmission process involves an electrical impulse called an action potential. An action potential can be described as all-or-none and as self-regenerating. Neuroscientists use other words such as a spike or an impulse for the action potential.
This is the currently selected item. When a stimulus reaches a resting neuron the neuron transmits the signal as an impulse called an action potential. An action potential is described as a sudden and spontaneous change or reversal in the membrane potential above a threshold value due to increased permeability of the cell membrane.
Encyclopedia of the Neurological Sciences Second Edition 2014. The muscle action potential triggers a sequence of actions that ultimately results in the contraction and relaxation of the muscle fiber. An action potential may be described as.
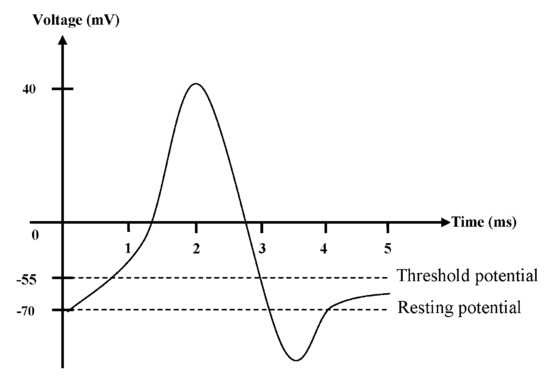
Which of the following best describes the role of Ca2 in muscle contraction. The resting potential is around -70 millivolts mV. What has been described here is the action potential which is presented as a graph of voltage over time in Figure 7.
In the neuron an action potential produces the nerve impulse and in the muscle cell it produces the contraction required for all movement. The change in the membrane voltage from 70 mV at rest to 30 mV at the end of depolarization is a 100-mV change. It binds to troponin moving tropomyosin so that myosin heads can bind to actin.
There have to be ion channels along the axon Rate of action potential depend upon capacitance axon diameter and density of ion channel. E the positive feedback loop for the sodium channel is terminated by the inactivation gate.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11522/Action_potential_curve.png)
Action Potential Definition Steps Phases Kenhub
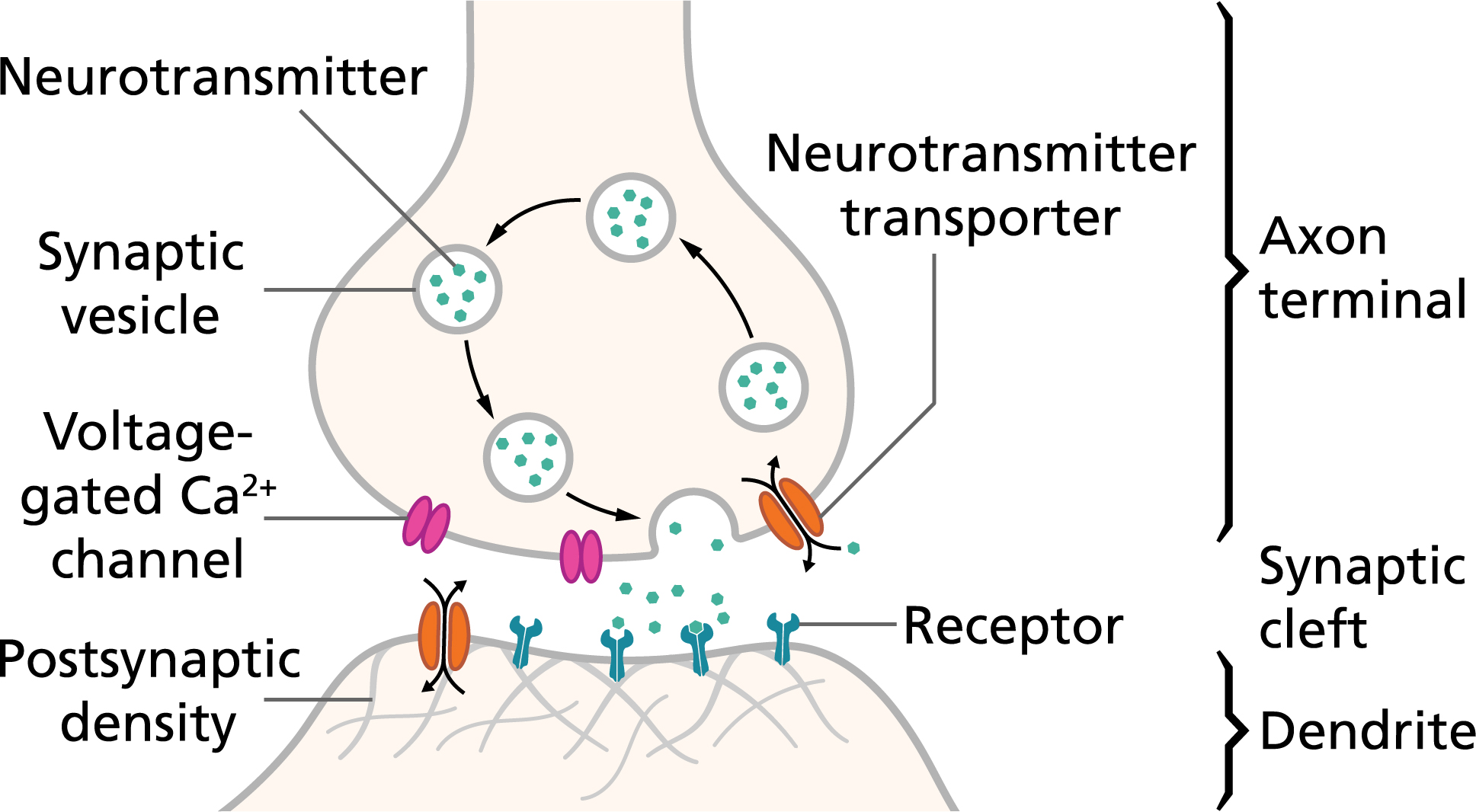
Action Potentials And Synapses Queensland Brain Institute University Of Queensland
Action Potentials And Synapses Queensland Brain Institute University Of Queensland
What Is An Action Potential Action Potential Chart Membrane Potential Molecular Devices

35 2b Nerve Impulse Transmission Within A Neuron Action Potential Biology Libretexts

Threshold Potential An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

10 5e The Action Potential And Propagation Medicine Libretexts

Cardiac Muscle Action Potential Diagram Explained Youtube

Question Video Describing The Series Of Events At A Neuromuscular Junction Nagwa

Threshold Potential An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Axon An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Temporal And Spatial Summation Difference Mechanism Facts
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11524/Action_potential_ions.png)
Action Potential Definition Steps Phases Kenhub

Action Potentials An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

35 2b Nerve Impulse Transmission Within A Neuron Action Potential Biology Libretexts

Action Potentials An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Ijms Free Full Text General Pathways Of Pain Sensation And The Major Neurotransmitters Involved In Pain Regulation Html


Comments
Post a Comment